
1998年、ASR(Automobile Shredder Residue)を機械的処理のみで完全に使用可能な材料にする処理方法のプロトタイプが、日本、欧州(EPC)、米国で出願され、それら3ヶ国で特許が成立しました。
2018年には、上記特許の主要な内容を継承し、新たな処理方法を考慮した上で、早期審査の結果、同年5月には国際特許、そして8月には、日本国内の特許が成立しました。2022年10月14日には米国特許、2023年2月15日には中国特許が査定されました。(成立しました。) 2024年1月8日には欧州特許庁(EPO)より、欧州特許条約(EPC)加盟39ヵ国の特許が査定されました。
日本では、2005年に自動車リサイクル法が施行されて以来、ASR(シュレッダーダスト:使用済み自動車を処理する際に発生する各種金属、有機物、無機物の混合物)の発生量が年間80万トンから40〜50万トンに減少しましたものの、2005年から今日までの16年間に日本で発生したASRのほとんどは、焼却処理(サーマルリアイクル)されて来ました。自動車リサイクル法が施行された当時には、ダイオキシン発生の問題は全く問題視されていませんでしたが、地球の温暖化が顕著になって来た現在では、焼却時に発生するCO2の量が、ダイオキシン発生問題(これも完全に抑えきっているとは言えません。)よりも大きな社会問題となって来ました。
年間40~50万トンのASRを焼却処理した場合、焼却によるCO2発生量は年間50~60万トンにもなります。これは、SDGsの考えに大きく反しています。
当社が特許を取得している機械処理による加工法では、鉄やアルミニウム、さらには貴重な銅などの金属を酸化させることなく選別することができます。(投入量の25%)また、弊社設計の3種類の分級機を使用することにより、塩素含有量が①0.3%以下、②0.30~0.50%、③0.5~0.7%で、焼却処理の際にダイオキシンの発生の触媒となる銅も殆ど含まれていない高品質のウレタンリッチな有機系残渣(投入量の50~60%)を得ることができます。このウレタンリッチの軽量残渣は、ケミカルリサイクルの原料にもなりますし、マテリアルリサイクルとして、・・・<詳細はお問い合わせ下さい。>・・・活性炭という有価物を作る原料にもなります。
それ故、この特許を使用したプラントから製造される有機・無機系残渣を、ケミカル&マテリアルリサイクルに利用すると、ダイオキシンの発生をゼロにするだけでなく、SDGsの最大の目的であるCO2のゼロエミッションを同時に達成することができることになります。
尚、CO2発生をゼロにすることはできませんが、高カロリーのウレタンリッチの有機系残渣 (重量比55~60%)をサーマルリサイクルに利用しますと、石炭やコークスを燃料や助燃材、そして還元剤として使用した場合に比較して、CO2の発生率を1/3(33%)下げることができると同時に、年間40~50トンの化石燃料を輸入しなくともよくなります。同時に、為替の変動による化石燃料の価格の上下動を心配しなくとも良くなるなどのメリットも生まれます。
その他の利用法としては、比重の重い無機系残渣(重量比25%)からPVC(塩化ビニールを)を抜いた混合残渣 (ガラス、小石、ゴム、プラスチック、タイヤ屑など)を、ウレタンリッチの軽量な有機系残渣(同上50~60%)と混ぜて固めると転炉の消泡材 (比重:1.5~1.8g/cm3)として使用することができます。
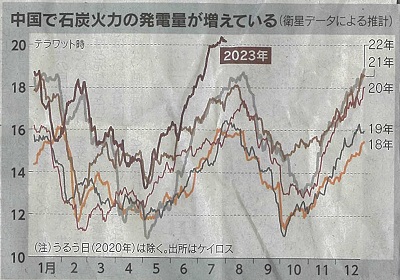
石炭火力の需要
日経2023年8月20日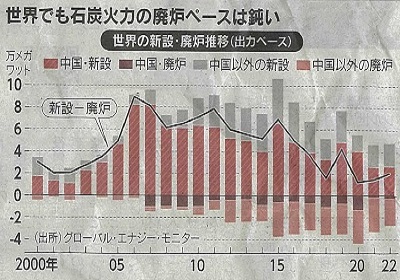
世界の石炭火力の廃炉ペースは鈍い
日経2023年8月20日
ウレタンリッチの有機系残渣(投入量の50~60%)をマテリアルリサイクルできる方法や適応できる分野はすでにいくつか見つけてありますが、ウレタンリッチの軽量残渣から新しいウレタンを製造できるメーカーやパートナーを探しています。現在、世界のほとんどの先進国が頭を悩ませているASRの持続可能なリサイクルシステムのためのコンソーシアムを形成するためにはウレタンメーカーの協力も不可欠です。
註:*寿命が来た防音壁は、スクラップ業者のヤードに搬入され、シュレッダーで破砕された後に、ASRではなく、SRの残渣として回収され、破砕と共に再度ウレタンリッチの有機系残渣として集塵機に分離回収された後に、吸音材や活性炭としてマテリアルリサイクル、プラスチック製造用オイルを製造するケミカルリサイクル、そして、石炭や助燃材やコークスの代替品又は、電炉でのコークスやフェロシリコンの代替品となる還元剤や転炉の消泡材、そして自治体の焼却場の助燃材としても使用することができます(サーマルリサイクル)。 つまり、これら三種類の分野でのリサイクル法の完成は、SDGsの趣旨に沿ったサーキュラーエコノミーの完成でもあります。
Keyword:ASR処理,シュレッダーダスト処理,ASR再資源化,メカ式ASR全量資源化,銅3%選別,時間6㌧処理年間12,000㌧処理可能に,SDGs,サーキュラーエコノミー,脱炭素・CO2削減効果あり,特許

In 1998, a prototype for a method of processing ASR (Automobile Shredder Residue) into fully usable materials solely through mechanical treatment was filed for patent in Japan, Europe (EPC), and the United States, and patents were granted in these three regions.
In 2018, inheriting the main content of the above patent and considering a new processing method, an international patent was granted in May of the same year following an expedited examination, and a Japanese domestic patent was granted in August. A US patent was granted on October 14, 2022, and a Chinese patent was granted on February 15, 2023. On January 8, 2024, the European Patent Office (EPO) granted a European patent covering 39 countries under the European Patent Convention (EPC).
In Japan, since the enforcement of the Automobile Recycling Law in 2005, the annual volume of ASR (shredded dust: a mixture of various metals, organic materials, and inorganic materials generated when end-of-life vehicles are processed) has decreased from 800,000 tons to 400,000-500,000 tons. However, over the 16 years from 2005 to the present, most of the ASR generated in Japan has been incinerated (thermal recycling).At the time the Automobile Recycling Law was enacted, the issue of dioxin emissions was not considered a significant problem, but with the current marked increase in global warming, the amount of CO2 generated during incineration has become a more significant social issue than the problem of dioxin emissions (which cannot be said to be completely controlled).
When 400,000-500,000 tons of ASR are incinerated annually, the CO2 emissions from incineration can reach 500,000-600,000 tons per year. This is highly contrary to the principles of the SDGs.
Our patented mechanical processing method allows for the selection of metals such as iron, aluminum, and valuable copper without oxidizing them (25% of the input). Additionally, using three types of classifiers designed by our company, we can obtain high-quality polyurethane-rich organic residues (50-60% of the input) with chlorine content of (1) 0.3% or less, (2) 0.30-0.50%, and (3) 0.5-0.7%, and almost no copper, which acts as a catalyst for dioxin generation during incineration. This polyurethane-rich lightweight residue can be used as a raw material for chemical recycling, material recycling, and as a raw material for producing valuable activated carbon.
Therefore, if the organic and inorganic residues produced by the plant using this patent are used for chemical and material recycling, it will not only reduce dioxin emissions to zero, but also achieve zero CO2 emissions, which is the main goal of the SDGs.
Although it is not possible to completely eliminate CO2 emissions, using high-calorie polyurethane-rich organic residues (55-60% by weight) for thermal recycling can reduce CO2 emissions by 1/3 (33%) compared to using coal, coke, or other fossil fuels as fuel, combustion aids, and reducing agents. This also eliminates the need to import 40,000-50,000 tons of fossil fuels annually and mitigates concerns about price fluctuations of fossil fuels due to exchange rate changes, among other benefits.
Other utilization methods include mixing heavy inorganic residues (25% by weight) from which PVC (polyvinyl chloride) has been removed with lightweight polyurethane-rich organic residues (50-60% as above) and solidifying them for use as a foaming agent in converters (specific gravity: 1.5-1.8g/cm³).

Global demand for coal-fired power 
Global coal-fired power plant closures pace is slow
Sorce:NIKKEI,20th,Aug.2023
We have already identified several methods and applicable fields for material recycling of organic residues rich in urethane (50-60% of input). However, we are looking for manufacturers or partners who can produce new urethane from lightweight residues rich in urethane. The cooperation of urethane manufacturers is also essential to form a consortium for a sustainable ASR (Automobile Shredder Residue) recycling system, which is a major concern for most developed countries in the world.
*Note:End-of-life soundproof walls are transported to scrapyard yards, shredded, and then collected as SR (Shredder Residue) rather than ASR (Automobile Shredder Residue). After being separated and collected as urethane-rich organic residues by dust collectors, they can be used for material recycling as sound-absorbing materials or activated carbon, chemical recycling to produce oil for plastic manufacturing, and thermal recycling as alternatives to coal, auxiliary fuel, or coke. Additionally, they can be used as reducing agents or defoaming agents for converters or as auxiliary fuel in municipal incinerators. In other words, completing recycling methods in these three fields also completes the circular economy in line with the SDGs (Sustainable Development Goals).
新特許/New Patent
(H30.3月出願/Applied in March,2018)

日本新特許証
Japan Patent
granted in 2018

国際(PCT)出願及び
国際調査報告書(A評価)
International(PCT) Patent
granted in 2018
(Evaluation A rank)

米国特許証
2022年10月14日査定
USA patent
granted 14th,Oct.2022

中国特許証
2023年2月15日査定
China patent
granted 15th,Feb.2023

欧州(EPC20ヵ国)特許証
2024年1月8日
EPC patent
granted 8th,Jan.2024
旧特許/Old Patent

米国特許証/USA 
EU特許証/EPO 
日本特許証/Japan
1998~2018年有効
Valid from 1998 to 2018.
Detailed information(Needed Password)